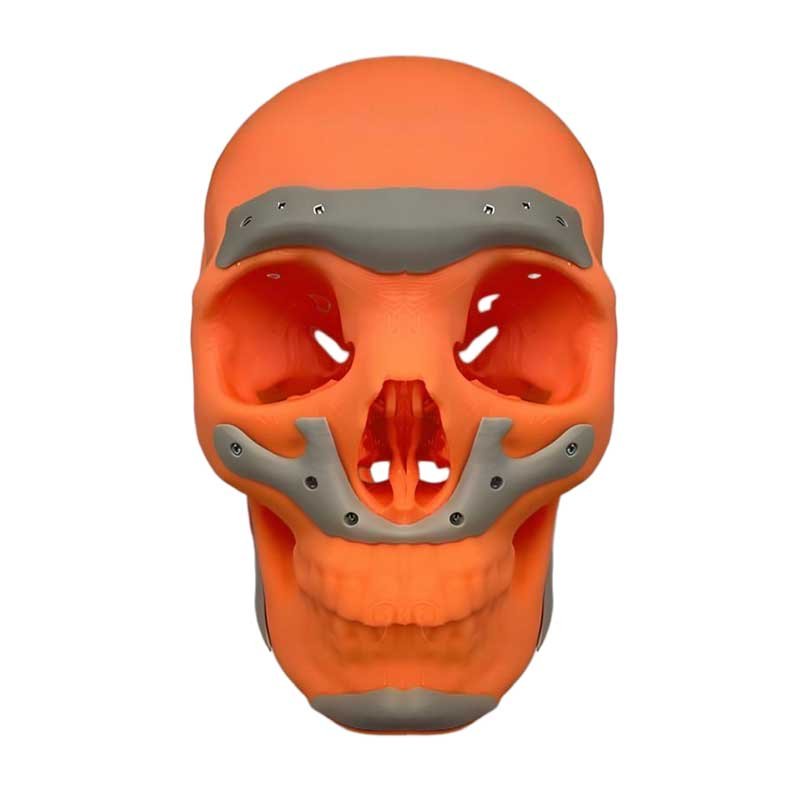
描述
Advantages of Medical Ceramic 3D Printing:
1.High Customization for Precise Patient Matching
Generates personalized implants (e.g., joint prostheses) directly from CT/MRI data, perfectly fitting bone defects and avoiding adaptability issues of traditional implants.
Designs exclusive shapes for complex anatomical structures (e.g., irregular bone defects, growing pediatric bones), enhancing treatment outcomes.2. Biocompatibility and Safety
Materials like hydroxyapatite and β-tricalcium phosphate mimic natural bone composition, inducing osteocyte adhesion/growth and promoting osseointegration while reducing rejection risks.
3. Controllable Mechanical Properties and Biomimetic Structures
Adjusts printing parameters (porosity, layer thickness, internal lattice) to match the mechanical strength (compression/bending resistance) of natural bone, minimizing “stress shielding” (bone atrophy from overly rigid traditional implants).
4. Improved Surgical Efficiency and Precision
Prints pre-surgical bone models or guides to assist in surgical planning and rehearsal, reducing operation time and intra-operative risks (e.g., complex fracture reduction, bone reconstruction after tumor resection).
5. High Material Utilization, Low Waste
Additive manufacturing deposits material only where needed, achieving over 90% material utilization for medical ceramics—far higher than traditional subtractive machining (which wastes >50% of material)—reducing costs, especially for expensive bioactive ceramics.
6. Support for Complex Structures and Functional Integration
Fabricates intricate geometries (hollow structures, gradient porosity, internal channels) unattainable by traditional methods, even integrating drug-delivery functions (loading antibiotics/growth factors in ceramic pores).
7. Reduced Post-Operative Complications
Implants that conform to bone surfaces minimize micromotion, wear, and interfacial inflammation, lowering risks of loosening or revision surgery.
| Product name | FormAlox 999 | FormAlox 998 | FormAcon 3Y |
| Product description | Engineering alumina parts, manufactured using LCM additive manufacturing method | Engineering zirconia parts, manufactured using LCM additive manufacturing method | |
| Material | Aluminum oxide (Al O2 3) | Aluminum oxide (Al O2 3) | Zirconium oxide (ZrO3 mol-% Y O2 3 stabilized) |
| Purity | 99.9 % | 99.8 % | 99.8 % |
| Density | 3.985 g/cm3 (99.4 % of theoretical density) | 3.985 g/cm3 (98.4 % of theoretical density) | 6.088 g/cm3 (99.4 % of theoretical density) |
| Hardness HV10 | 1550 | 1550 | 1250 |
| Bending strength | 430 MPa (4-point) | 400 MPa (4-point) | 930 MPa (4-point) |
| Young‘s modulus | 300 GPa | 380 GPa | 205-210 GPa |
| CTE | 7-8 ppm/K | 7-8 ppm/K | 10 ppm/K |
| Thermal conductivity | 37 W/mK | 29 W/mK | 2.5-3 W/mK |
| Surface roughness Ra | ~ 0.4 µm | 0.9 µm | ~ 0.3 µm |
| Max. operating temp. | 1650 °C | 1650 °C | 1500 °C |
| Color | White | White | White |
| Size | Max.: 84.9 x 51.4 x 156.8 mm Wall thickness: up to 4 mm | Max.: 84.9 x 51.4 x 156.8 mm Wall thickness: up to 5 mm | |